The US Fed is facing the heat of the rising pressure on the US inflation rate and the Fed governor has now become the butt of all jokes. There was a time when the governor delayed rate hikes considering the inflation to be transitory. The rationale was right to an extent. The demand for used cars had risen significantly after the pandemic and a lot could be blamed on the shortage of semiconductor chips and the supply chain pressures which worsened things. However, this continued crisis put pressure on the Fed and now it is being heavily criticized for its faulty planning and decision-making.
Let’s understand how serious the problem is and how the US economy can come out of this problem.
Inflation Rate
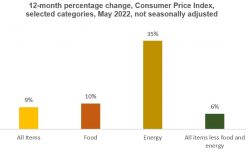
The fight against inflation has been a prolonged process and the Fed’s decision to hike interest rates by 75 basis points was not surprising. However, it is to be noted that this is the highest rate hike in the last three decades. The pressure on fuel prices and gasoline has triggered a sharp rise in inflation for the current period. US gasoline prices have reached USD 5 for the first time. President Biden understands the energy crisis and has requested dealers to increase supply. Powell, in his latest speech, recognized the need for demand destruction to bring price stability which is needed for economic growth.
Unemployment
Demand for labor is more than the supply and this is putting pressure on wages. This in turn increases the cost of production and businesses will end up having margin contraction. While there was a continued rise in the demand for jobs, the supply of resources increased modestly during the same period. As a result, the labor market tightened further between December and May, with job gains averaging 488,000 per month and the unemployment rate falling from 3.9% to 3.6%.
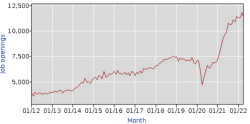
Housing prices
The biggest companies in the real estate market of the USA are finding a difficult time to survive. Home prices are now 34% higher than they were a couple of years ago and the mortgage rates add to the pressure. While the federal funds rate does not directly affect the long-term mortgage rates, it does have an impact on the credit cards and adjustable rate mortgages (ARM). Higher interest rates will trigger a slowdown in consumer spending.
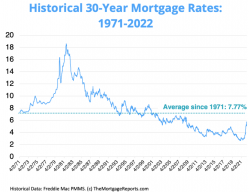
- The housing market has witnessed immense pressure since 2020 as buyers were willing to pay for a new house when borrowing costs were close to zero. This also increased the price of commodities like lumber. The demand for housing is expected to improve and stay strong as first-time home buyers represent the largest share (31 percent), according to data from the National Association of Realtors (NAR). The supply and demand imbalance is likely to continue putting more upward pressure on the prices of the housing market. One key mistake that the Fed is blamed for is when the prices of houses were increasing by ~50 percent in major metropolitan areas, they were purchasing mortgage-backed securities (MBS).For those who are not familiar with MBS, let’s discuss this concept here.
What are Mortgage-Backed Securities?
- A mortgage-backed security is a financial instrument that is backed by collateral in the form of mortgage loans.
- The bank provides loans to a customer and then sells these loans at a discount to the investment industry.
- Government-backed entities like Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac bundle these loans into something called MBS and sell them to investors.
- The investment industry offers MBS as an investment opportunity to investors. The investor who buys mortgage-backed security is essentially lending money to home buyers. In return, the investor gets the rights to the value of the mortgage, including interest and principal payments made by the borrower.
- Banks act as intermediaries between borrowers and MBS investors. When they sell the loans to the investment company, they will no longer have the concern to obtain repayment of the loan from the borrower.
The Fed still owns a huge chunk of the market for MBSs, but it is gradually selling off its holdings. MBS holdings as of June 15th, 2022 have increased by 99 percent from
Registration Open - Analyst Program Click here
Economic activity
Real gross domestic product (GDP) is reported to have surged at a 6.9% annual rate in the fourth quarter of 2021 and then to have declined at a 1.5% annual rate in the first quarter. Private final domestic demand has been relatively stable which indicates that there is demand from consumers.
Quantitative Tightening – the need of the hour?
The Federal Reserve reduced its monthly asset purchase since last November and further accelerated this in December. The Fed is conscious about the size of the Balance Sheet and announced in May that it will significantly reduce its security holdings and these reductions would begin from the 1st of June. The Fed is often criticized for increasing the Balance Sheet size during the time of the pandemic.
Daily transactions in the reverse repo facility have been northwards of USD 2 Trillion. This has increased from USD 1.5 Trillion at the beginning of the year. Large banks like JP Morgan Chase find it more convenient to deposit the funds with the Fed instead of keeping the cash on their balance sheet. This in turn impacts the return ratios for the banks. The Fed has been playing a key role in sucking this excess liquidity from the system. This liquidity was at a time introduced by the central bank when the economy faced the wrath of pandemic.
M2 is a measure of the U.S. money stock that includes M1 (currency and coins held by the nonbank public, checkable deposits, and travelers’ checks) plus savings deposits (including money market deposit accounts), small-time deposits under $100,000, and shares in retail money market mutual funds.
It is seen that the M2 balance in May 2022 has increased by 40 percent as compared to the balance in March 2020.
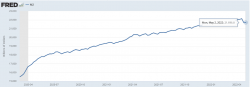
The Fed’s Balance Sheet currently stands at ~USD 9 trillion and looks stable. This is about 36 percent of the nominal GDP.
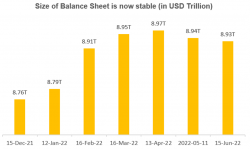
Caught in the vicious cycle
Alastair Borthwick, Chief Financial Officer of Bank of America, informed in the latest earnings call that they have deposits of about USD 2 trillion and they have never been so liquid. On an aggregated basis, average deposit balances were up 47% from pre-pandemic levels and 15% higher than 2021.
The bank’s management feels that high wage growth has triggered this for customers in different income groups.
Probability of US economy recession
The country is fearful of recession. Economists typically expect a recession is coming when the economy endures two or more consecutive quarters of decline, in terms of the growth rate of the country’s gross domestic product (GDP). Moreover, there are signs of flattening of the yield curve with the 10-2 Year Treasury Yield Spread indicating that the investors are not optimistic about the long term growth and would like to invest on the front end of the curve.
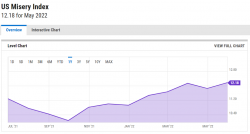
Misery index is often used as a reference point to measure the financial wellbeing of an average American citizen. It is basically the sum of unemployment rate and inflation. Currently it stands at such elevated levels that it’s higher than several post-World War II recessions.
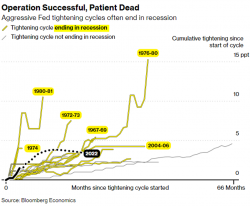
Jerome Powell will continue to get criticized for some of the decisions that were mistimed but a lot will depend on the supply chain crisis, geopolitical pressures and the vicious cycle may continue to torment the Fed governor.
Other Trending Posts in this Series – Volcker Moment | HUL | Tesla Valuation
To stay updated about all of our posts on Businesses and Finance Careers – register and create a free account on our website. You will also get access to a free Finance Bootcamp course once you register.