Zomato is a major player in food delivery market, a duopoly market with high growth potential and low penetration. Only 10% of Indians with internet access have used online food delivery, compared to 38% in the US and 53% in China.
Zomato is a leading foodtech company that started out as a restaurant search and discovery platform and later ventured into food delivery.
Aggregators like Zomato are critical for the growth of the food service industry in India as around 94% of restaurants in India are standalone in nature and do not have the financial resources and manpower to manage a dedicated delivery fleet. It also enables restaurant partners to market, engage, and acquire customers without requiring large teams with digital marketing and branding expertise.
The company connects users, restaurants, and delivery providers to meet their needs. Core business offerings includes:
- Food Delivery
- Dining out
- Zomato Pro
- Hyper pure
- Quick commerce (Blinkit)
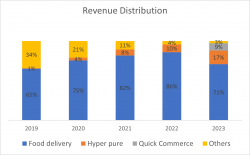
Segment that drives Zomato’s revenue
Zomato’s revenue from operations have grown 5x over the last 5 years from Rs.13 billion in FY19 to Rs.71 billion.
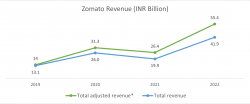
Adjusted Revenue = Revenue from operations as per financials plus customer delivery charges
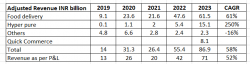
1.Food Delivery
Zomato earns nearly 70% of its revenue from food delivery which is growing at a CAGR of 60% from FY19 to FY23. Customers can place orders on Zomato’s platform, which are fulfilled by Zomato’s delivery executives. Zomato charges restaurants a take rate which is fixed at a percent of the average order value (AOV). Currently, the take rate is at ~17%. Furthermore, Zomato earns advertising revenue from restaurants that advertise on the app.
Zomato has stopped accounting for delivery fee charged to customers in its revenue and treat it as pass through to delivery executives.
The segment is primarily driven by an increase in order volume and average order value over the period, which are increasing at a CAGR of 36% and 10% respectively.
2. Hyper pure
This is the B2B segment of Zomato under which Zomato supplies fresh produce to restaurants. Zomato sources these ingredients directly from the farmers and producers and then supplies them to the restaurants.
Zomato offers more than 1200 ingredients and kitchen products across various categories such as fruits & vegetables, groceries, dairy products, poultry products, beverages and bakery products to its
From FY19 to FY23, Hyper pure’s revenue grew by 250%, which is consistent with the 155% growth in the number of Restaurant Partners.
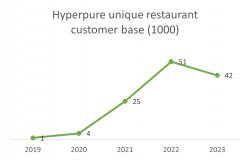
3.Other sources of revenue include:
- Dining out
Under this segment, Zomato offers customers search and discovery of restaurants, table bookings, and payment options. It is currently not monetizing its services. This business earns revenues only from advertisement sales where restaurant partners pay the Zomato for enhanced visibility on its platform.
- Zomato Gold
Zomato gold is a paid-membership program launched in January 2023. Under this program, customers receive several benefits like free delivery, VIP access during peak times and no delay guarantee for a fee. As of 31st March FY23, Zomato Gold has scaled to 1.8 million members. Zomato Gold members comprise as much as ~30% of total GOV (Mar-23), however, the order frequency of these customers has on an average increased by ~60% post becoming members.
- Other businesses
Other businesses such as Nutrition, Fitso and international operations in countries other than India and UAE have been discontinued during FY22.
- Blinkit
Zomato acquired blinkit in August 2022, establishing its presence in the quick commerce category.
What about the profitability?
Zomato is an EBITDA Negative company. Despite this, Zomato has been able to reduce its adjusted EBITDA loss from INR 21 billion loss in 2019 to INR 7.8 billion loss in 2023. Zomato’s food delivery business has been inching closer to profitability. While all segments of Zomato experience an EBITDA loss, quick commerce accounts for nearly 3/4th of the loss.
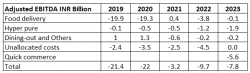
*Adjusted EBITDA = EBITDA + share-based payment expense – rental paid for the period pertaining to Ind AS 116 leases
Note: Unallocated costs include server & tech infrastructure costs, corporate salary costs and other corporate overheads.
What about the Expenses?
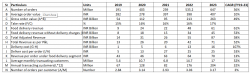
Zomato’s largest expenses in FY23 were Delivery and related charges, Employee costs, Cost of good sold and Advertisement and sales promotion, accounting for 75% of the total costs.
Delivery and related charges include the total availability fees paid to the delivery partners, the cost of delivery partner’s call centre and the cost of consumables. This cost is directly related to the order volumes. Employee benefit expenses increased by 120% in FY22, primarily due to increases in ESOP expenses to the tune of INR 7.4 billion. Employee cost came down in FY23 on account of lower ESOP charges. Digital marketing and refunds to merchants and customers are major components of advertising and sales promotion expenses.
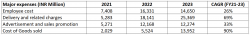
In order for Zomato to become profitable, these costs need to go down. The company has increased its average delivery expense charged to customers to compensate for the increase in delivery and related charges. Sales and advertising expenses are expected to decline as competitive intensity in the business stabilizes with a duopoly market structure. In FY 22, Zomato acquired approximately 50% of its new customers organically thanks to its user-generated reviews and restaurant listings.
Now the question is, how has the acquisition of Blinkit will improve the growth prospects for Zomato?
Zomato acquired Blinkit formerly known as Grofers in an all-stock deal worth Rs 4,448 crore
The acquisition of Blinkit expands the company’s presence into a highly competitive quick commerce segment. Quick commerce refers to delivering a wide range of groceries/FMCG products in a span of 15 to 20 minutes to customers.
At USD 5.5 billion, Quick Commerce represents just 1% of the USD620 billion grocery market. Redseer estimates that it will surge 10-15x in size by 2025E with an addressable market of USD45b.
Zomato decided to buy a quick commerce business instead of building it in-house after two failed attempts at building it since 2020.
Quick commerce is a natural extension to both the major businesses of Zomato. Quick commerce and Food Delivery are hyperlocal in nature and Hyperpure’s existing partnership with several vendors can be used to supply in dark stores.
This acquisition will help Zomato to widen the services offered, increase the addressable market, increase customer wallet share spent on its platform, drive higher frequency and engage customers as well as aid in delivery fleet optimization.
Blinkit app will continue to operate independently. Over time, management plans to integrate delivery fleet backends to increase delivery efficiency.
Financials Metrics of Blinkit:
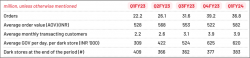
Quarter on Quarter, there has been an increase in the number of monthly transacting customers. This has led to an increase in revenue and GOV.
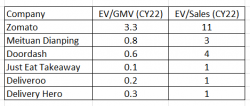
What is Zomato’s Valuation in Comparison to its Global Peers?
Zomato at a market cap of approximately 1,15,000 crores is trading at a significant premium when compared with its global peers. It is important to note that each company has a different revenue recognition policy, making a simple comparison insufficient. Moreover, Zomato is the fastest-growing company in terms of revenue growth and gross merchandise volume, additionally its average order value compared to per capita income is lowest leaving a room for significant growth in future.
Concluding remark:
On our final note, we cannot predict when Zomato will become profitable, but it is essential for Zomato to increase average order value, increase take rates, increase the number of orders per customer and reduce customer discounts to improve profitability and cash generation.
Furthermore, we should note that since working capital is negative and there are no major capital expenditure requirements, the entire positive EBIT will flow into free cash flow.
Zomato may take a while to become profitable but it is tackling a real issue, so it is likely to last.