Do you know that more than half (53%) of product searches start on Amazon and only 23% start on search engines? And many of those searches are likely to lead to Amazon.
Even better, customers complete 28% of purchases on Amazon in three minutes or less, and half of all purchases are finished in less than 15 minutes.
But over the years, Amazon has evolved into more than just an online store. While e-commerce makes up a significant portion of its overall sales, several other business segments are fuelling its growing revenue.
Business Segments and Revenue Contribution

- Online-stores: This segment includes sales generated via website/app and generates ~50%+ of the company’s revenue.
- Physical Stores: This segment is small and generates just ~4%+ of the company’s revenue. Amazon operates ~620 stores worldwide (primarily Whole Foods).
- Third-Party seller services (3P): The interesting piece of Amazon’s revenue model generates ~20%+ of the company’s revenue. In this category, the vendors sell products through Amazon’s online marketplace. And the company earns a fee for every unit sold. Here the company provides two options to sellers:
- Fulfilment by Merchant: In this category, the vendor stores and ship products directly to customers. Amazon charges shipping rates to vendors based on the product category and shipping services selected by customers.
- Fulfilment by Amazon: In this category, Amazon manages logistics and warehousing of the products. And charge fulfilment fee to vendors, including picking and packaging charge, shipping and handling, customer service, and product return charges per unit sold. They also charge an inventory storage fee to vendors based on the volume of inventory.
- Subscription Services: Amazon offers a bundle of digital services, including prime video, prime music, and prime reading, and charge a subscription fee. The bundling provides an edge over others in the OTT space. A recent Letter to Shareholders 2020 mentioned that Amazon has 200 million Prime members. This segment generates ~7% of the company’s revenue.
- AWS: The company is a market leader in cloud-based infrastructure with a 31% market share and offers storage, database, and analytics services to its B2B clients. This segment is a cash cow for Amazon. However, this segment generates just ~12% of the company’s revenue but extremely profitable. We will see that in the next segment.
- Others: This primarily includes advertising revenue or revenue from co-branded credit cards.
At this point, it is critical to understand which segment(s) drives revenue and which segment(s) drives profitability.
So, let’s understand the revenue part – if we see the last 5 years growth, then we can clearly see that Online stores demonstrated the least growth (obviously, the base is large, so on a consolidated level, it still matters). Other segments are growing at a breakneck speed.
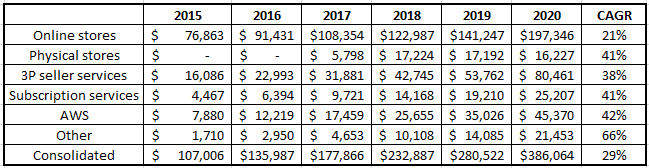
All values are in USD million
Also, it is interesting to note that the Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) of retail sales on Amazon in 2020 was ~$490 Bn and 3P generate close to 60% of GMV (Letter to Shareholders 2018), that is ~$300 Bn, and the revenue from 3P was $80 Bn, so that means a rack rate of ~27%. (Meaning, for every $100 worth of sales through Amazon, they keep $27). More platform users, higher leverage and hence higher margin (or sustain the margins). Now you know why a Prime subscription is cheap? It is simple; it gives Amazon a strong subscribers base to attract more sellers to the platform.
Registration Open - Analyst Program Click here
Is Amazon dependent on any specific geography?
Region-wise revenue split
- United States: ~68%
- Germany: ~8%
- UK: ~7%
- Japan: ~5%
- Rest (including India): ~12%
Amazon’s dependency on India is pretty low at this point. India contributes ~0.5% of the company’s revenues.
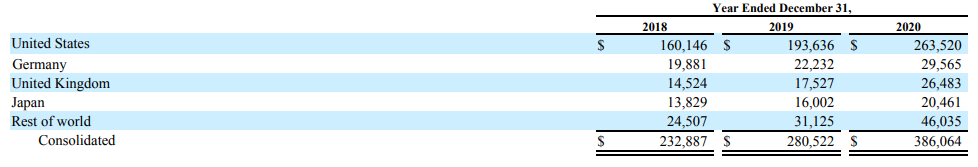
All values are in USD million
Finally, on the profitability – which segment is more profitable for Amazon?
In this, there are three segments.
-
North America
- Revenue contribution ~61%
- Operating Margin under 4% (and reducing since last three years)
- Contribution to overall Operating Income ~37% (North America Operating Income/Amazon’s Operating Income)
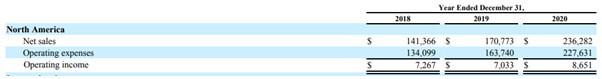
All values are in USD million
-
International
- Revenue contribution ~27%
- Operating Margin under 1% (profitable for the first time in 2020)
- Contribution to overall Operating Income ~3% (International Operating Income/Amazon’s Operating Income)
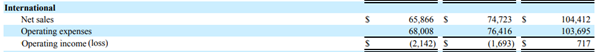
All values are in USD million
-
AWS
- Revenue contribution ~11%
- Operating Margin ~30% (and almost constant for so many years)
- Contribution to overall Operating Income ~60% (AWS Operating Income/Amazon’s Operating Income)

All values are in USD million
To summarize, the total operating margin for the company is ~6%, and AWS is its cash cow because of its high operating margins. It generates 12% of sales for the company but contributes 60% to operating profits with a margin of 30%. Compared to North America and International that contributes 33% and 3%, respectively. Now you know why AWS is so so important for Amazon.
So, in a nutshell, Amazon is dominating the retail e-commerce space, and it is also a market leader in a cloud-based infrastructure. It also ranks 2nd in the OTT space in terms of the number of subscribers. It would be interesting to watch Amazon in streaming war and how it uses it as a funnel to drive its core business.
Other Trending Posts in this Series – Spotify | Netflix | Microsoft
To stay updated about all of our posts on Businesses and Finance Careers – register and create a free account on our website. You will also get access to a free Finance Bootcamp course once you register.